Getting Started with Raspberry Pi SBCs

Introduction
If you are into embedded systems and IoT development, I'm sure you've heard people say that the Raspberry Pi is the next step once you have a good grounding with microcontroller-based development boards such as Arduino, STM32, and ESP32. In this tutorial, we will be looking at the Raspberry Pi ecosystem. We will learn about what they are, who makes them, how we can use them, and what they can be used for.
Whether you are a newbie in embedded systems and IoT or you want to upgrade your skills in the field, this tutorial series has you covered.
What is Raspberry Pi
Raspberry Pi is a series of small single-board computers (SBCs) developed in the United Kingdom by the Raspberry Pi Foundation in association with Broadcom. The Raspberry Pi project was originally started to promote the teaching of basic computer science in schools.
Currently, there are various Raspberry Pi boards of different sizes and specs to tailor to different needs, ranging from being used as a desktop computer to media streaming, learning how to program, robotics, embedded AI, and IoT development, etc., the list goes on.
The Raspberry Pi has always been known as a processor-based single-board computer platform, but with the invention of the RP2040 microcontroller in 2020, which powers the Raspberry Pi Pico board, the Raspberry Pi has you covered, whether is project is controller-based or more advanced to require an SBC.
Raspberry Pi Boards
In this tutorial series, we will be working mainly with the latest in the Raspberry Pi SBC line-up, which is the Raspberry Pi 5.
You can check out the complete list and specs of all available boards on the Raspberry Pi website
Raspberry Pi 5
Raspberry Pi 5 is the latest model in the Raspberry Pi SBC lineup. With 2–3× the speed of the previous generation, and featuring silicon designed in‑house for the best possible performance, redefining the Raspberry Pi experience. It comes with an I/O-controller designed in-house, a power button, and an RTC chip, among other things. The Pi 5 is the desired board for this course.

Raspberry Pi 5
Pi 5 Specifications:
-
Broadcom BCM2712 2.4GHz quad-core 64-bit Arm Cortex-A76 CPU, with cryptography extensions, 512KB per-core L2 caches and a 2MB shared L3 cache
-
VideoCore VII GPU, supporting OpenGL ES 3.1, Vulkan 1.2
-
Dual 4Kp60 HDMI® display output with HDR support
-
4Kp60 HEVC decoder
-
LPDDR4X-4267 SDRAM (2GB, 4GB, 8GB, and 16GB)
-
Dual-band 802.11ac Wi-Fi®
-
Bluetooth 5.0 / Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
-
microSD card slot, with support for high-speed SDR104 mode
-
2 × USB 3.0 ports, supporting simultaneous 5Gbps operation
-
2 × USB 2.0 ports
-
Gigabit Ethernet, with PoE+ support (requires separate PoE+ HAT)
-
2 × 4-lane MIPI camera/display transceivers
-
PCIe 2.0 x1 interface for fast peripherals (requires separate M.2 HAT or other adapter)
-
5V/5A DC power via USB-C, with Power Delivery support
-
Raspberry Pi standard 40-pin header
-
Real-time clock (RTC), powered from external battery
-
Power button
.jpg)
Raspberry Pi GPIO Pins
Raspberry Pi GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output) pins are versatile digital pins on the Raspberry Pi board that can be used for various purposes, including input, output, PWM, I2C, SPI, UART, and more. These pins are crucial for interfacing with other components like sensors, motors, LEDs, and other electronic devices. We refer to this as physical computing. Raspberry Pi's GPIO pins are highly flexible and can be configured for various functions, making them suitable for a wide range of electronic projects.
Pin Numbering:
-
Physical Pin Numbering: Refers to the actual pin numbers on the Raspberry Pi's GPIO header. The Raspberry Pi typically has a 40-pin header (on models like Raspberry Pi 5, 4, 3, and 2).
-
Broadcom (BCM) Numbering: Refers to the GPIO pin numbers as defined by the Broadcom SoC (System on Chip) used in the Raspberry Pi. This numbering is commonly used in software when controlling the GPIOs.
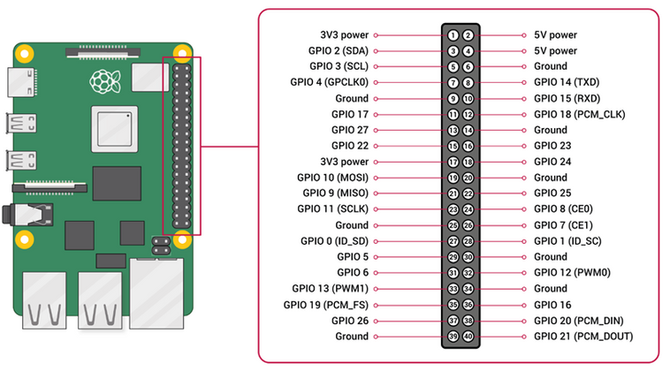
Raspberry Pi GPIO Pin Diagram
Pin Types:
1. Power Pins:
-
3.3V Pins (Pin 1, Pin 17): These provide a constant 3.3V output, used to power small components that require 3.3V.
-
5V Pins (Pin 2, Pin 4): These provide a constant 5V output, used to power components that require 5V.
-
GND (Ground) Pins: These are connected to the ground of the system, used as a reference point for voltage and as a return path for current.
2. GPIO Pins:
-
General I/O: The basic use of GPIO pins is as input or output pins. When set as an output, the pin can be set high (3.3V) or low (0V). When set as input, the pin can read high or low states.
-
Special Functions: Some GPIO pins have alternate functions such as PWM (Pulse Width Modulation), I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit), SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface), and UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter).
GPIO Pin Functions:
1. Digital Input/Output: Pins can be configured to read digital signals (high or low) or output digital signals.
2. PWM Output GPIO18 (Pin 12), GPIO12 (Pin 32), GPIO13 (Pin 33): Some GPIO pins can output PWM signals, which are useful for controlling devices like servos or LEDs with varying brightness.
3. I2C Interface GPIO2 (Pin 3) and GPIO3 (Pin 5): Pins dedicated to the I2C communication protocol, typically used for connecting sensors and other peripherals.
-
SDA (Data Line): Used for transmitting data.
-
SCL (Clock Line): Used for synchronizing data transmission.
4. SPI Interface GPIO10 (Pin 19), GPIO9 (Pin 21), GPIO11 (Pin 23): Used for high-speed communication with peripherals like ADCs, DACs, and displays.
-
MOSI (Master Out Slave In): Data sent from the master to the slave.
-
MISO (Master In Slave Out): Data sent from the slave to the master.
-
SCLK (Serial Clock): Clock signal generated by the master.
-
CE (Chip Enable): Selects the slave device.
5. UART Interface GPIO14 (Pin 8) and GPIO15 (Pin 10): Serial communication pins used for transmitting (TX) and receiving (RX) data.
6. Ground (GND): Pins used to establish a reference voltage and return path for the circuit.
Raspberry Pi 5 Accessories
1. Power Supply
The Raspberry Pi 5 can be powered through the Type-C USB port on the board using either a battery pack or a power plug. The recommended power rating is 25-30 Watt or 5V/5Amps.

Official 27W USB Type-C Power Supply for Raspberry Pi
2. Active cooler
The Raspberry Pi Active Cooler for Raspberry Pi 5 is a dedicated clip-on cooling solution for Raspberry Pi 5. It combines an aluminium heatsink with a temperature-controlled blower fan to keep your Raspberry Pi 5 at a comfortable operating temperature, even under heavy loads.

Raspberry Pi 5 Active cooler
2. Raspberry Pi 5 Case
The Raspberry Pi Case for Raspberry Pi 5 is a clip-together four-part enclosure with an active cooling fan. It keeps your Raspberry Pi 5 at a comfortable operating temperature even under heavy load.

Raspberry Pi 5 Case
